Generate Certificate From Public Key
Apr 12, 2019 Windows 8.1 Product Key is one of the most efficient and widely used application all over the world in the field of Windows activation. It posses the best tools and most amazing features along with the the most exceptional techniques that makes it the ideal application that provides the best solution to activate Microsoft Windows 8 or 8.1. Feb 09, 2020 Windows 8.1 Activator + Product Key Generator Free Download 2019. Windows 8.1 Activator a good software for non-active windows. There are many types of window activator and reloader all over the world. But Generator is an authenticated and recommended generator for windows activated. It makes your windows registered. Windows 8.1 Product Key Generator can utilize to make the activator key like the Microsoft in the product key and can utilize most of the recent version.In contrast, users can use the utility in exceptionally in the mainstream since the user can use the inclusive kinds of methods. Download windows 8.1 product key generator free online. Feb 04, 2020 The Windows 8.1 product key is the latest revision for Windows 8 users. In this case, you are using Windows 8 and want many more features in your operating system. Microsoft released an update for Windows 8.1 that includes additional traditional and attractive features. Oct 20, 2019 Window 8.1 Product Key Generator + Crack Free Download 2020. Windows 8.1 has many different versions. Different functions offer ISO in each of these window edition. Below you will see the Product Keys of every version and comparison of the various available Windows 8.1 packages. The fact that there is a mirror digitalrivercontent.net is downloaded directly from Microsoft.
-->- Generate Certificate From Public Key Certificate
- Public Key Private Key Certificate
- Generate Certificate From Public Key Online
Aug 18, 2015 This P7B can be used as the 'public key' in AccessData products. AD Enterprise, the AccessData Agent, and Site Server all require a public and private key pair to function. If you use IIS to generate or otherwise house your certificates, you may need to extract your private/public key pair to use with AccessData products.
Adds a certificate to a database in SQL Server.
Be sure to properly destroy and wipe the old key file. Creating a new file with a new passphrase will not help if the old file remains available. Videos illustrating use of PuTTYgen Using PuTTYgen to generate an SSH key. Using PuTTYgen to generate an SSH key. How to set up PuTTY SSH keys for passwordless logins using Pagent. Sep 11, 2018 The first thing to do would be to generate a 2048-bit RSA key pair locally. This pair will contain both your private and public key. You can use Java key tool or some other tool, but we will be working with OpenSSL. To generate a public and private key with a certificate signing request (CSR), run the following OpenSSL command. Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority Use the key file you created in the procedure above to generate the certificate signing request (CSR). You send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain a signed certificate. In a typical public-key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the certificate issuer is a certificate authority (CA), usually a company that charges customers to issue certificates for them. By contrast, in a web of trust scheme, individuals sign each other's keys directly, in a format that performs a similar function to a public key certificate.
This feature is incompatible with database export using Data Tier Application Framework (DACFx). You must drop all certificates before exporting.
Syntax
Arguments
certificate_name
Is the name for the certificate in the database.
AUTHORIZATION user_name
Is the name of the user that owns this certificate.
ASSEMBLY assembly_name
Specifies a signed assembly that has already been loaded into the database.
[ EXECUTABLE ] FILE = 'path_to_file'
Specifies the complete path, including file name, to a DER-encoded file that contains the certificate. If the EXECUTABLE option is used, the file is a DLL that has been signed by the certificate. path_to_file can be a local path or a UNC path to a network location. The file is accessed in the security context of the SQL Server service account. This account must have the required file-system permissions.
Important
Azure SQL Database does not support creating a certificate from a file or using private key files.
BINARY = asn_encoded_certificate
ASN encoded certificate bytes specified as a binary constant.
Applies to: SQL Server 2012 (11.x) and later.
WITH PRIVATE KEY
Specifies that the private key of the certificate is loaded into SQL Server. This clause is invalid when the certificate is being created from an assembly. To load the private key of a certificate created from an assembly, use ALTER CERTIFICATE.
FILE ='path_to_private_key'
Specifies the complete path, including file name, to the private key. path_to_private_key can be a local path or a UNC path to a network location. The file is accessed in the security context of the SQL Server service account. This account must have the necessary file-system permissions.
Important
This option is not available in a contained database or in Azure SQL Database.
BINARY = private_key_bits
Applies to: SQL Server (Starting with SQL Server 2012 (11.x)) and Azure SQL Database.
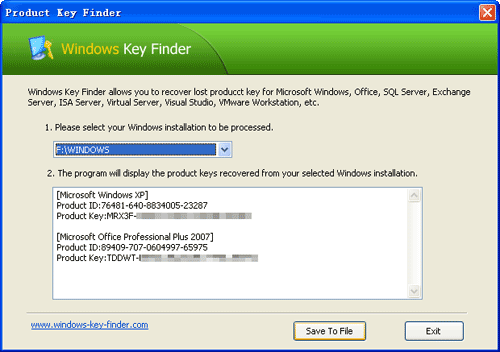 They include office SharePoint server 2007 and Office Groove networks.
They include office SharePoint server 2007 and Office Groove networks.
Private key bits specified as binary constant. These bits can be in encrypted form. If encrypted, the user must provide a decryption password. Password policy checks are not performed on this password. The private key bits should be in a PVK file format.
DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'key_password'
Specifies the password required to decrypt a private key that is retrieved from a file. This clause is optional if the private key is protected by a null password. Saving a private key to a file without password protection is not recommended. If a password is required but no password is specified, the statement fails.
ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'password'
Specifies the password used to encrypt the private key. Use this option only if you want to encrypt the certificate with a password. If this clause is omitted, the private key is encrypted using the database master key. password must meet the Windows password policy requirements of the computer that is running the instance of SQL Server. For more information, see Password Policy.
SUBJECT = 'certificate_subject_name'
The term subject refers to a field in the metadata of the certificate as defined in the X.509 standard. The subject should be no more than 64 characters long, and this limit is enforced for SQL Server on Linux. For SQL Server on Windows, the subject can be up to 128 characters long. Subjects that exceed 128 characters are truncated when they are stored in the catalog, but the binary large object (BLOB) that contains the certificate retains the full subject name.
START_DATE = 'datetime'
Is the date on which the certificate becomes valid. If not specified, START_DATE is set equal to the current date. START_DATE is in UTC time and can be specified in any format that can be converted to a date and time.
EXPIRY_DATE = 'datetime'
Is the date on which the certificate expires. If not specified, EXPIRY_DATE is set to a date one year after START_DATE. EXPIRY_DATE is in UTC time and can be specified in any format that can be converted to a date and time. SQL Server Service Broker checks the expiration date. Backup with Encryption using certificates also checks the expiration date and will not allow a new backup to be created with an expired certificate, but will allow restores with an expired certificate. However, expiration is not enforced when the certificate is used for database encryption or Always Encrypted.
ACTIVE FOR BEGIN_DIALOG = { ON OFF }
Makes the certificate available to the initiator of a Service Broker dialog conversation. The default value is ON.
Remarks
A certificate is a database-level securable that follows the X.509 standard and supports X.509 V1 fields. CREATE CERTIFICATE can load a certificate from a file, a binary constant, or an assembly. This statement can also generate a key pair and create a self-signed certificate.
Generate Certificate From Public Key Certificate
The Private Key must be <= 2500 bytes in encrypted format. Private keys generated by SQL Server are 1024 bits long through SQL Server 2014 (12.x) and are 2048 bits long beginning with SQL Server 2016 (13.x). Private keys imported from an external source have a minimum length of 384 bits and a maximum length of 4,096 bits. The length of an imported private key must be an integer multiple of 64 bits. Certificates used for TDE are limited to a private key size of 3456 bits.
The entire Serial Number of the certificate is stored but only the first 16 bytes appear in the sys.certificates catalog view.
The entire Issuer field of the certificate is stored but only the first 884 bytes in the sys.certificates catalog view.
The private key must correspond to the public key specified by certificate_name.
When you create a certificate from a container, loading the private key is optional. But when SQL Server generates a self-signed certificate, the private key is always created. By default, the private key is encrypted using the database master key. If the database master key does not exist and no password is specified, the statement fails.
The ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD option is not required when the private key is encrypted with the database master key. Use this option only when the private key is encrypted with a password. If no password is specified, the private key of the certificate will be encrypted using the database master key. If the master key of the database cannot be opened, omitting this clause causes an error.
You do not have to specify a decryption password when the private key is encrypted with the database master key.
Note
Built-in functions for encryption and signing do not check the expiration dates of certificates. Users of these functions must decide when to check certificate expiration.
A binary description of a certificate can be created by using the CERTENCODED (Transact-SQL) and CERTPRIVATEKEY (Transact-SQL) functions. For an example that uses CERTPRIVATEKEY and CERTENCODED to copy a certificate to another database, see example B in the article CERTENCODED (Transact-SQL).
The MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA, and SHA1 algorithms are deprecated in SQL Server 2016 (13.x). Up to SQL Server 2016 (13.x), a self-signed certificate is created using SHA1. Starting with SQL Server 2017 (14.x), a self-signed certificate is created using SHA2_256.
Permissions
Requires CREATE CERTIFICATE permission on the database. Only Windows logins, SQL Server logins, and application roles can own certificates. Groups and roles cannot own certificates.
Examples
A. Creating a self-signed certificate
The following example creates a certificate called Shipping04. The private key of this certificate is protected using a password.
B. Creating a certificate from a file
The following example creates a certificate in the database, loading the key pair from files.
Important
Azure SQL Database does not support creating a certificate from a file.
C. Creating a certificate from a signed executable file
Alternatively, you can create an assembly from the dll file, and then create a certificate from the assembly.
Important
Azure SQL Database does not support creating a certificate from a file.
Important
Public Key Private Key Certificate
Starting with SQL Server 2017 (14.x), the 'CLR strict security' server configuration option prevents loading assemblies without first setting up the security for them. Load the certificate, create a login from it, grant UNSAFE ASSEMBLY to that login, and then load the assembly.
D. Creating a self-signed certificate
The following example creates a certificate called Shipping04 without specifying an encryption password. This example can be used with Parallel Data Warehouse.
See Also
Generate Certificate From Public Key Online
ALTER CERTIFICATE (Transact-SQL)
DROP CERTIFICATE (Transact-SQL)
BACKUP CERTIFICATE (Transact-SQL)
Encryption Hierarchy
EVENTDATA (Transact-SQL)
CERTENCODED (Transact-SQL)
CERTPRIVATEKEY (Transact-SQL)
CERT_ID (Transact-SQL)
CERTPROPERTY (Transact-SQL)