Generate Ssh Public Key Centos
Apr 18, 2018 SSH, or secure shell, is an encrypted protocol used to administer and communicate with servers. When working with a CentOS server, chances are, you will spend most of your time in a terminal session connected to your server through SSH. This guide will show you how to generate SSH key-pair to set up password-less authentication on CentOS/RHEL 7.
Introduction
Secure Shell (SSH) is an encrypted protocol used by Linux users to connect to their remote servers.
You can generate an SSH key pair directly in cPanel, or you can generate the keys yourself and just upload the public one in cPanel to use with your hosting account. When generating SSH keys yourself under Linux, you can use the ssh-keygen command. To do so follow these steps: Open up the Terminal. May 24, 2019 SSH keys can serve as a means of identifying yourself to an SSH server using public-key cryptography and challenge-response authentication. The major advantage of key-based authentication is that in contrast to password authentication it is not prone to brute-force attacks and you do not expose valid credentials, if the server has been compromised. Once the distinct key pair has been generated, the next step remains to place the public key on the virtual server that we intend to use. Users would be able to copy the public key into the authorizedkeys file of the new machine using the ssh-copy-id command. Feb 11, 2017 In this video i demonstrated how to generate a ssh key on centos 7.
Generally, there are two ways for clients to access their servers – using password based authentication or public key based authentication.
Using SSH keys for authentication is highly recommended, as a safer alternative to passwords.
This tutorial will guide you through the steps on how to generate and set up SSH keys on CentOS 7. We also cover connecting to a remote server using the keys and disabling password authentication.
1. Check for Existing Keys
Prior to any installation, it is wise to check whether there are any existing keys on the client machines.
Open the terminal and list all public keys stored with the following command:
The output informs you about any generated keys currently on the system. If there aren’t any, the message tells you it cannot access /.ssh/id_*.pub , as there is no such file or directory.
2. Verify SSH is Installed
To check if thw package is installed, run the command:
If you already have SSH, the output tells you which version it is running. Currently, the latest version is OpenSSH 8.0/8.0p1.
Note: Refer to our guide If you need to install and enable SSH on your CentOS system.
Steps to Creating SSH keys on CentOS
Step 1: Create SSH Key Pair
1. Start by logging into the source machine (local server) and creating a 2048-bit RSA key pair using the command:
If you want to tighten up security measures, you can create a 4096-bit key by adding the -b 4096 flag:
2. After entering the command, you should see the following prompt:
3. To save the file in the suggested directory, press Enter. Alternatively, you can specify another location.
Note: If you already have a key pair in the proposed location, it is advisable to pick another directory. Otherwise it will overwrite existing SSH keys.
4. Next, the prompt will continue with:
Although creating a passphrase isn’t mandatory, it is highly advisable.
5. Finally, the output will end by specifying the following information:
Now you need to add the public key to the remote CentOS server.
You can copy the public SSH key on the remote server using several different methods:
Guitar pro 6 user key id generator. Open Guitar Pro 6; Enter your User ID and Key ID; Select 'Offline activation' The software generates a long key that is valid for this computer only. Now copy this long key to avoid mistakes. At this point you need a computer with internet access. Go to this page Paste your first offline key; Validate A new key has been generated. Save this new key. Guitar Pro 6 Keygen is a legendary editor who can add multitrack to guitar rhythms and shows the bass and trouble graph on the score meter. Guitar Pro 6 Crack is a tool for musicians and guitarists they are editing their sound quality with multi-type effects. The operating system does not matter you can easily run it on MAC and Windows, Linux as well as it is capable of every type of OS. Jul 22, 2015 serialkey preview: teamzwt aeaak-anr60-aaaaz or user id = 5int1747410 key id = annaa-bhawb-4bnn9 user id = 5int5674774 key id = hekz6-8b4ex-498b7 or user id.
- using the ssh-copy-id script
- using Secure Copy (scp)
- manually copying the key
The fastest and easiest method is by utilizing ssh-copy-id. If the option is available, we recommend using it. Otherwise, try any of the other two noted.
1. Start by typing the following command, specifying the SSH user account, and the IP address of the remote host:
If it is the first time your local computer is accessing this specific remote server you will receive the following output:
2. Confirm the connection – type yes and hit Enter.
3. Once it locates the id_rsa.pub key created on the local machine, it will ask you to provide the password for the remote account. Type in the password and hit Enter.
4. Once the connection has been established, it adds the public key on the remote server. This is done by copying the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file to the remote server’s ~/.ssh directory. You can locate it under the name authorized_keys.
5. Lastly, the output tells you the number of keys added, along with clear instructions on what to do next:
1. First, set up an SSH connection with the remote user:
2. Next, create the ~/.ssh directory as well as the authorized_keys file:
3. Use the chmod command to change the file permission:
chmod 700 makes the file executable, while chmod 600 allows the user to read and write the file.
4. Now, open a new terminal session, on the local computer.
5. Copy the content from id_rsa.pub (the SSH public key) to the previously created authorized_keys file on the remote CentOS server by typing the command:
With this, the public key has been safely stored on the remote account.
1. To manually add the public SSH key to the remote machine, you first need to open the content from the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file:
2. As in the image below, the key starts with ssh-rsa and ends with the username of the local computer and hostname of the remote machine:
3. Copy the content of the file, as you will need later.
4. Then, in the terminal window, connect to the remote server on which you wish to copy the public key. Use the following command to establish the connection:
5. Create a ~/.ssh directory and authorized_keys file on the CentOS server with the following command:
6. Change their file permission by typing:
7. Next, open the authorized_keys file with an editor of your preference. For example, to open it with Nano, type:
8. Add the public key, previously copied in step 2 of this section, in a new line in (under the existing content).
9. Save the changes and close the file.
10. Finally, log into the server to verify that everything is set up correctly.
Once you have completed the previous steps (creating an RSA Key Pair and copying the Public Key to the CentOS server), you will be able to connect to the remote host without typing the password for the remote account.
All you need to do is type in the following command:
If you didn’t specify a passphrase while creating the SSH key pair, you will automatically log in the remote server.
Otherwise, type in the passphrase you supplied in the initial steps and press Enter.
Once the shell confirms the key match, it will open a new session for direct communication with the server.
Although you managed to access the CentOS server without having to provide a password, it still has a password-based authentication system running on the machine. This makes it a potential target for brute force attacks.
You should disable password authentication entirely by following the outlined steps.
Note: Consider performing the following steps through a non-root account with sudo privileges, as an additional safety layer.
1. Using the SSH keys, log into the remote CentOS server which has administrative privileges:
2. Next, open the SSH daemon configuration file using a text editor of your choice:
3. Look for the following line in the file:
4. Edit the configuration by changing the yes value to no. Thus, the directive should be as following:
5. Save the file and exit the text editor.
6. To enable the changes, restart the sshdservice using the command:
7. Verify the SSH connection to the server is still functioning correctly. Open a new terminal window and type in the command:
In this article, you learned how to generate SSH key pairs and set up an SSH key-based authentication. We also covered copying keys to your remote CentOS server, and disabling SSH password authentication.
Next, You Should Read:
SSH (Secure Shell) is an encrypted protocol that is way more secure than Plain text based protocols like Telnet, however, it’s could be vulnerable if not configured properly.
We are assuming that you have root permission, otherwise, you may start commands with “sudo”.
We are going to provide 4 simple tips to get a more secure SSH protocol on your CentOS server.
Changing SSH Port
To change the Standard listening Port, you have to change the SSH Server configurations with the command below. We are using nano editor in this tutorial, you may use your own editor if you wish.
Then you need to edit the line that refers to the port number, for that you have to follow the instruction below.
Then change the port number from 22 to your preferable port (e.g. 2022) And press Ctrl +O and Ctrl +X in order to save and exit.
What you need to do is enable the newly created port through Firewall to do that follow the instructions below.
If you run the command above and get an error that semanage command not found, run the commands below to install it.
And then run the semanage command again to allow the new port
After that you need to allow the new port through the firewall with the command below:
Disable root logins
You’ll be adding a layer of security to your SSH server if you disable root user logins. It would be more secure to brute force attacks or in case your password is stolen.
First, you need to create a non-root user with the following instructions:
Then open the ssh configuration file with your editor. (we are using nano)
Then change the Highlighted line from “PermitRootLogin yes” to “PermitRootLogin no”
Crtl+O Crtl+X
Create a key-based Authentication SSH connection
If your Server is accessible over the Internet, you can use public key authentication instead of passwords, because SSH key authentication with password phrase is way more secure than password-only authentication, while a password can eventually be cracked with a Brute-force attack or keyloggers.
Depending on your client OS you should follow the instructions to create a pair of authentication keys.
Ssh Public Key Windows
If you are using Windows:
You have to download the Putty key generator (a.k.a Puttygen)
Here is the recommended download link:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html
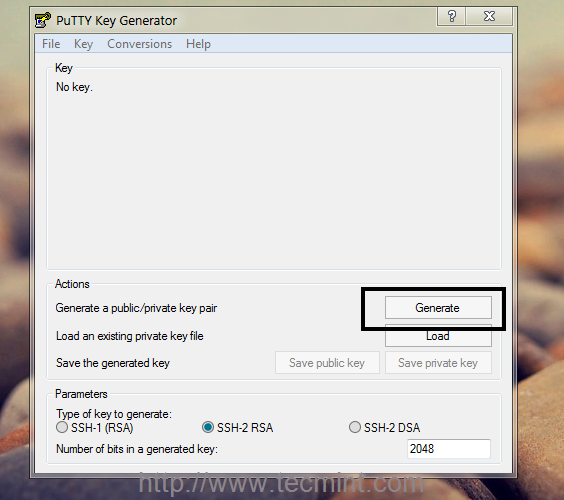
- Open PuTTYgen utility.
- For Type of key to generate, select SSH-2 RSA
- In the Number of bits in a generated key field is refer to how complicated you want your key to be, you can change the value between 2048 to 4096 for make more complicated key.
- After selecting your settings click on Generate to start Process.
- Move your mouse pointer around in the blank area of the Key section, below the progress bar (to generate some randomness) until the progress bar is full.
- A private and public key pair has now been generated.
- (Optional): it’s also recommended to set a passphrase for your key.
- Save Private and Public keys
CAUTION: be careful with choosing the path you saving the keys, if you lose them and username/password logins are disabled on your server, you might lose your access to your server.
- Then open your Putty, expand the SSH category and click on “Auth”
- In “private key file for authentication” browse your Private key.
- Finally, you should copy the Public key file in your server in this path: ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
If you are using Linux
–To generate an RSA key pair
- Accept the default file location of /.ssh/id_rsa. Entering a passphrase is recommended
- The public key is written to ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub The private key is written to ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- Copy the contents of ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub from client system into the file ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on the Server.
- You may use “cat” command on the client side to view the file and use an editor like “nano” on the server side to modify or create the authorized_keys file.
- After all, it’s recommended to disable the Password authentication as well.
Uncomment these lines and change them refer to the line below:
Disable SSH Protocol 1
SSH has two versions that may use, SSH v1 is older and less secure than protocol SSHv2 2, it’s recommended to be disabled unless you specifically need it.
Nfs payback key generator download. Jan 29, 2018 Need for Speed Payback Key Generator Descriptions: We made this 100% secure Need for Speed Payback Crack Download. Proxy and Anti Ban systems are enabled automatically when you run the Free Key Generator Need for Speed Payback. We will update this tool whenever necessary. You will automatically receive this update.
Centos Ssh Key Setup
Uncomment the line
and change it to:
Centos Ssh Authorized Keys
Now we restart the SSH service so our new configuration take place.